

A low Accounts Payable Turnover Ratio may indicate that a company is experiencing cash flow problems, supplier relationship issues or may be taking advantage of extended payment terms. However, other factors such as industry standards, payment terms, and business models can impact the ratio. It indicates that a company is paying its creditors faster and more frequently than a company with a low ratio.
#Accounts payable turnover ratio how to#
How to Interpret Accounts Payable Turnover Ratio ResultsĪ high Accounts Payable Turnover Ratio is generally considered positive. On the other hand, if a company negotiates shorter payment terms, it may have a higher turnover ratio as it pays off its accounts payable more quickly.
For example, if a company negotiates longer payment terms with its suppliers, it may have a lower turnover ratio as it takes longer to pay off its accounts payable. Payment terms can vary from supplier to supplier and can have a significant impact on the ratio.

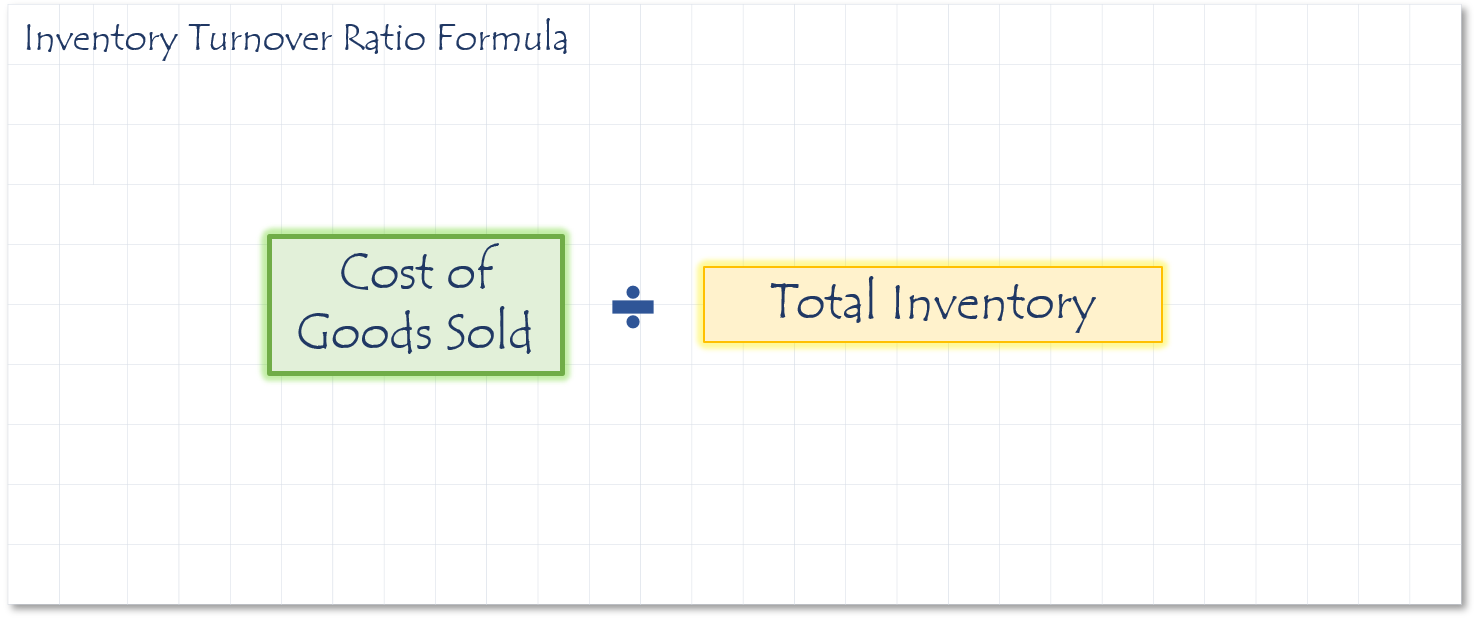
On the other hand, a low accounts payable turnover ratio may indicate that a company is not paying its suppliers in a timely manner, which could damage relationships with suppliers and affect the availability of credit in the future. It is important to note that a high accounts payable turnover ratio may indicate that a company is paying its suppliers too quickly, which could lead to cash flow problems. To calculate the average accounts payable outstanding, you can add the beginning and ending accounts payable balances and divide the sum by two. This can be calculated using the following formula:Īccounts Payable Turnover Ratio = Total Purchases / Average Accounts Payable Outstanding The formula for calculating the Accounts Payable Turnover Ratio is simple: divide the total purchases by the average accounts payable outstanding during the period under review. How to Calculate Accounts Payable Turnover Ratio By monitoring this ratio, companies can take proactive steps to improve their payment processes and avoid potential financial difficulties. If the ratio is decreasing over time, it may indicate that the company is struggling to pay its bills on time, which can lead to a cash crunch. In contrast, a low Accounts Payable Turnover Ratio may indicate that a company is not paying its creditors on time, which can lead to damage relationships, loss of discounts, and even legal consequences.Īnother important aspect of the Accounts Payable Turnover Ratio is that it can help a company identify potential cash flow issues. A high Accounts Payable Turnover Ratio indicates that a company has an efficient and timely payment system, which is important in maintaining a good relationship with vendors and suppliers. It is an essential financial metric as it reflects the effectiveness of the company's credit and payment policies. The Accounts Payable Turnover Ratio measures the number of times a company pays its accounts payable during a given period, typically a year. What is Accounts Payable Turnover Ratio and Why is it Important? Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) to Measure the Effectiveness of Your Accounts Payable Process.Examples of Successful Companies with High Accounts Payable Turnover Ratios.How to Compare Your Company's Accounts Payable Turnover Ratio with Industry Averages.Best Practices for Monitoring and Managing Accounts Payable Turnover Ratio.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
